
Midline shift is measured in millimeters, as the perpendicular distance between a midline structure usually the septum pellucidum and a line designated the midline. Before the advent of cross sectional imaging, midline shift was assessed by displacement of the calcified pineal gland on a frontal radiograph of the skull 2. Midline shift describes the situation where the midline of the intracranial anatomy is no longer in the midline and is the result of pushing or pulling forces within either side of the intracranial compartment (see Figure 1). Midline shift is a finding described on transverse (axial) slices from CT and MRI studies 1. This can be fatal.Midline shift brain prognosis Midline shift brain WHAT ELSE ARE WE WORRIED ABOUT?īrain herniation is a lethal complication of this type of intracranial bleeding. WAS THERE A WAY TO PREVENT IT?Īvoiding the initial trauma will prevent this condition from occurring (however this is not always practical). Patents who are diagnosed and treated quickly have a good prognosis.
Neurosurgical evacuation (i.e. surgical drainage of blood) is often the emergent treatment for this type of cranial bleeding. Mannitol is an osmotic diuretic that decreases intracranial pressure/volume temporarily. This is only a temporary measure of controlling increased intracranial pressure. Hyperventilation that brings the PCO2 down to 25/30 mmHg will cause cerebral vasoconstriction and can reduce intracranial volume/pressure quickly. **Reducing intracranial pressure is key to preventing brain herniation** The arrow heads outline the lens shaped bleeding, and the arrow points out the skull fracture ( source) HOW DO WE RULE OTHER DIAGNOSES OUT? HOW DO WE TREAT IT? Appearance of epidural hematoma on a CT scan. Learn more about how this condition looks radiologically here. It does not cross the suture lines of the skull, but can cross the fall and tentorium. It often shows a biconvex (lentiform/”lens-shape”) blood collection that is hyper dense. Non-contrast CT scan is the imaging modality of choice for intracranial bleeding/hemorrhagic stroke. Hemiparesis on the contralateral side of the brain injury. A fixed dilated pupil can often be seen in patients with a epidural hemorrhage ( source) A fixed dilated pupil (“blown pupil) can be present on the ipsilateral side of this injury. Other presentations/chief complaints can include:Ĭranial nerve III damage/palsy can be the result of this condition. Coma/mental status changes/neurological symptoms occur after the lucid interval (when intracranial pressure increases).Lucid period of several hours where the patient regains consciousness and does not notice anything out of the ordinary.Initial injury that is typically associated with brief loss of consciousness.Risk factors: recent head trauma, male, rare in patients younger then 2 years old or greater then 60 years old.Ĭlassic presentation often involves 3 major phases: Rupture of an artery in this location leads to rapid expansion of the hematoma which can lead to hemorrhagic stroke, and even transtentorial brain herniation.
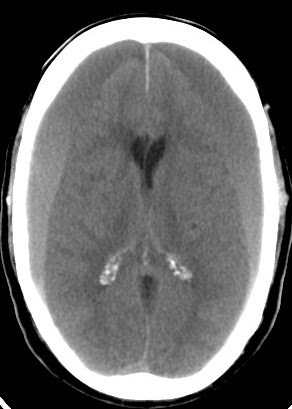
Anatomical different between an epidural and subdural hematoma ( source) WHY IS IT A PROBLEM? This is often secondary to fracture of the temporal bone.
#Subdural hematoma blown pupil archive#
11 ARCHIVE OF STANDARDIZED EXAM QUESTIONSĪn epidural hematoma refers to bleeding that occurs between the dura meningeal layer and the skull (the bleeding will separate the dural from the bone. It is classically caused by the rupture of the middle meningeal artery, although more chronic presentations can be caused by venous bleeding.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
